How to Write a Structured Literature Review? A Step-by-Step for PhD & Academic Research
Kenfra Research - Bavithra2025-10-28T16:39:58+05:30Writing a structured literature review is one of the most important milestones in academic research, especially for graduate students and PhD scholars. A well-structured literature review not only highlights the current knowledge on a topic but also identifies the literature gap your research aims to fill. Whether you’re preparing a PhD literature review or contributing to a research paper, a structured format ensures clarity, coherence, and academic rigor.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through the process of writing a structured literature review, covering essential methodologies, tools, writing strategies, and formatting tips to enhance your academic writing skills.
What is a Structured Literature Review?
A structured literature review is a methodical and organized approach to summarizing, analyzing, and synthesizing existing research on a specific topic. Unlike a simple summary or narrative literature review, the structured format follows a clear framework—often aligned with the research question, methodology, or theoretical model.
Types of Literature Reviews
Before diving into the process, it’s important to understand the key types of literature reviews:
- Systematic Literature Review: A rigorous review focusing on pre-defined questions and inclusion/exclusion criteria.
- Narrative Literature Review: A qualitative summary of studies without a strict structure.
- Thematic Literature Review: Organizes sources based on recurring themes or concepts.
- Structured Literature Review: Combines the systematic approach with flexibility in synthesis and presentation.
Each type contributes differently to your research methodology and should be chosen based on your study objectives.
Steps to Write a Structured Literature Review
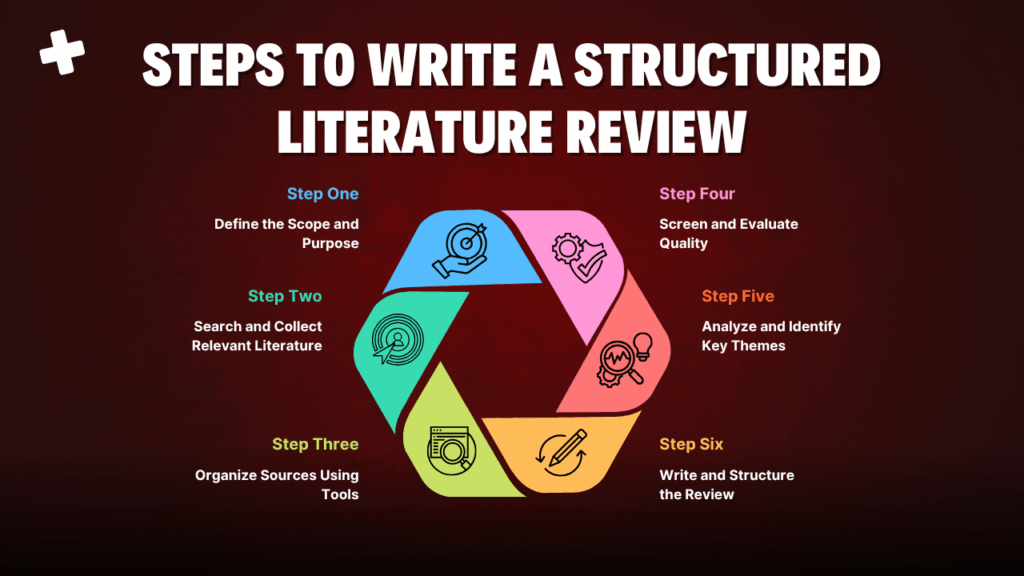
1. Define the Scope and Purpose
Start by identifying your research focus. Ask yourself:
- What is the objective of this review?
- What are the boundaries (time frame, region, population, topic)?
This clarity will help align your sources with your research question.
2. Search and Collect Relevant Literature
Use academic databases such as:
- Google Scholar
- PubMed
- JSTOR
- IEEE Xplore
- Scopus
Apply Boolean operators, filters, and keywords (e.g., “literature review methodology,” “structured review”) to narrow your results. This step is crucial for a systematic literature review in social sciences or sciences.
3. Organize Sources Using Tools
Use citation managers like:
- Zotero
- Mendeley
- EndNote
These tools simplify referencing and help you in writing a literature review using citation managers. You can also create folders or labels to sort articles by themes, methodologies, or chronological order.
4. Screen and Evaluate Quality
Not all articles are worth including. Apply inclusion/exclusion criteria based on:
- Peer-reviewed status
- Relevance to your topic
- Research design
- Year of publication
- Citations and author credibility
This helps you build a solid base for literature synthesis.
5. Analyze and Identify Key Themes
Start grouping studies based on:
- Similar findings
- Conflicting perspectives
- Methodological approaches
- Research populations
6. Find Gaps in Existing Research
Ask:
- What questions remain unanswered?
- Where is evidence lacking or contradictory?
This process leads to a meaningful literature gap analysis and shapes your research direction.
7. Write and Structure the Review
Your review should include:
- Introduction: Purpose, scope, structure
- Main Body: Organized by themes, trends, or chronology
- Synthesis Section: Connect findings, highlight debates
- Conclusion: Summarize insights and present the research gap
Make sure to follow a consistent citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.), especially if submitting to academic journals or as part of your thesis.

Tools and Techniques for Academic Writing
Effective review writing relies not only on research but also on the use of digital tools that improve workflow and consistency. Whether you’re preparing for a PhD research process or a graduate research project, these techniques enhance your scientific writing:
- Use AI-assisted tools for grammar and paraphrasing
- Visualize findings with concept maps or charts
- Regularly back up your sources and notes
Example: Structured Literature Review for PhD
If you’re doing a structured literature review example for PhD, your focus should include:
- Broad scope of databases
- Mixed-method literature
- Deep literature synthesis
- A strong guideline for writing a research literature review relevant to your discipline
Structure it clearly using headings and subheadings, and include visuals like tables for comparison.
Tips to Strengthen Your Review
- Maintain objectivity and neutrality in tone
- Avoid overloading with quotes—synthesize instead
- Connect findings to your research framework development
- Ensure consistency in terminology
- Ask for feedback from peers or academic mentors
These practices are particularly important for those seeking dissertation support or publishing in peer-reviewed journals.
Final Thoughts
Writing a structured literature review is not just about summarizing existing work—it’s about analyzing trends, revealing gaps, and establishing the scholarly value of your research. With the right approach, tools, and understanding of review writing techniques, you’ll create a strong foundation for your thesis, research paper, or PhD dissertation.







Leave a Reply