How to Write an Abstract? A Complete Guide for Research and Thesis
Kenfra Research - Bavithra2025-08-19T16:22:12+05:30Writing an abstract is a very important part of academic writing. If you are a student, researcher, or scholar, you’ll often need to summarize your work for journals, conferences, or dissertations. Understanding how to write an abstract effectively helps you present your work in a clear, concise, and compelling way.
In this blog, we will explain how to write an effective abstract, discuss different types, and provide tips and examples to help you succeed. Whether it’s for a thesis, dissertation, or journal submission, this guide will walk you through everything you need.
Overview of Effective Abstract Writing for Researchers
What is an Abstract?
An abstract is a brief summary of a research paper, thesis, dissertation, or academic article. It gives a short summary of the goals, methods, findings, and conclusion of the study. Think of it as a snapshot that helps readers quickly understand the essence of your research.
Why Abstracts Matter?
- First impression for readers, reviewers, and publishers.
- Helps in academic indexing and journal databases.
- Summarizes complex research into a digestible format.
- Plays a key role in whether your work gets read or cited.
Types of Abstracts
Abstracts can vary depending on the discipline and publication. The most common types include:
- Descriptive Abstract – Provides an overview of what the paper contains without going into detailed results. These are short and often under 150 words.
- Informative Abstract – Summarizes the purpose, methodology, findings, and conclusion. This type is most commonly used in research papers and dissertations.
- Critical Abstract – Adds commentary or evaluation of the research, often highlighting strengths and limitations.
- Structured Abstract – Organized under subheadings like Background, Methods, Results, and Conclusion, frequently used in scientific journals.
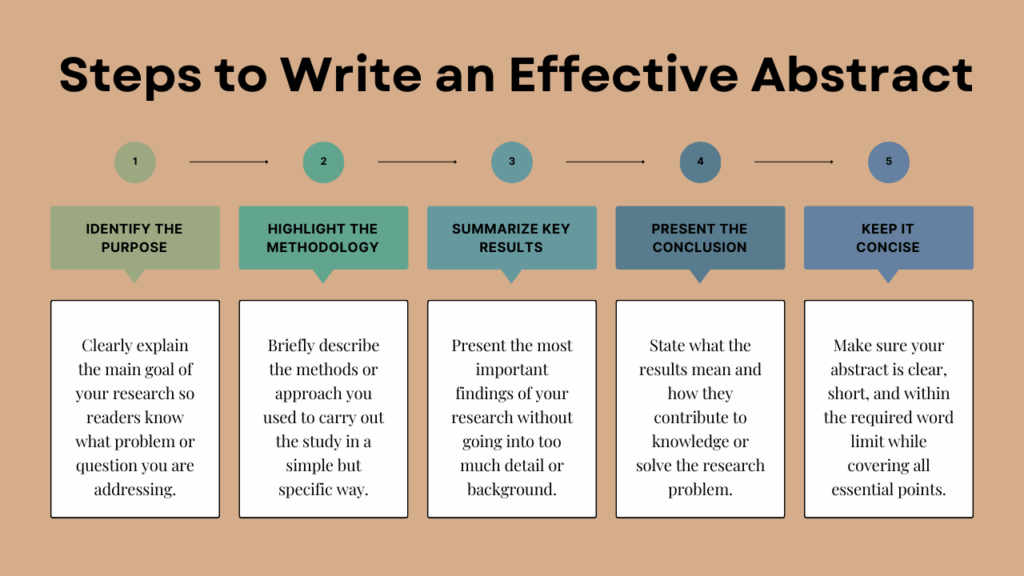
Steps to Write an Effective Abstract
Now let’s break down the step-by-step guide to writing an abstract:
1. Identify the Purpose
Clearly state the aim of your research. For example: This study investigates the impact of social media marketing on consumer behavior. This sentence sets the stage for the reader.
2. Highlight the Methodology
Briefly explain the research design, approach, or methods used. For instance, whether you used qualitative interviews, quantitative surveys, or a mixed-methods approach.
3. Summarize Key Results
Provide the major findings without unnecessary detail. Stick to numbers or main outcomes where possible.
4. Present the Conclusion
State the significance of your research and how it contributes to knowledge. This is where you show why your study matters.
5. Keep It Concise
Abstracts are usually 150–250 words, depending on the journal or institution guidelines. A strong abstract should give just enough information for the reader to decide if they want to explore the full paper.
Tips for Abstract Writing
Here are some tips for writing a clear abstract:
- Use clear and concise language.
- Avoid unnecessary jargon or complex vocabulary.
- Write in the past tense when describing completed research.
- Don’t include references, tables, or figures.
- Ensure the abstract stands on its own without requiring the full paper.
- Revise multiple times to refine clarity and readability.
Common Mistakes in Abstract Writing
Even experienced writers can make mistakes when drafting an abstract. Some pitfalls to avoid include:
- Writing too much detail, making it longer than needed.
- Including references or citations, which don’t belong in an abstract.
- Using vague language instead of precise terms.
- Not aligning with journal abstract format requirements.
- Forgetting keywords that improve search visibility.
Abstract vs Introduction
Many confuse abstracts with introductions, but they serve different purposes.
- Abstract: A short summary of the whole paper, covering purpose, method, results, and conclusion. It is self-contained and appears before the paper.
- Introduction: Provides background, context, and a review of related literature. It does not summarize results or conclusions.
Understanding this difference ensures that both sections complement each other without overlap.

Examples of Effective Abstracts
Reading examples of abstracts in research papers can be helpful. Here’s a sample:
This paper explores the role of artificial intelligence in healthcare. Using a mixed-method approach, we analyzed patient data from 20 hospitals. Findings suggest AI improves efficiency by 35%. The study concludes with recommendations for future AI-driven healthcare models.
Notice how the example is concise, covers purpose, method, results, and conclusion without unnecessary detail.
Tools and Resources for Abstract Writing
Today, students and researchers can use digital tools to refine their abstracts. Kenfra Research offer guidance for improving academic writing. Online resources also provide abstract examples, structured formats, and word count checkers to ensure compliance with submission guidelines.
Final Thoughts
Knowing how to write an effective abstract is essential for academic success. Whether for a thesis, dissertation, or journal, your abstract should be clear, concise, and compelling. Remember, the abstract is often the first thing readers will see—make it count.
By applying strategies, avoiding common mistakes, and learning from real examples, you’ll master the art of writing an academic abstract that stands out. With practice, writing abstracts will become a natural skill that supports your overall research and publishing journey.








Leave a Reply