What Hackers Look for First in Your CRM?
Kenfra Research - Bavithra2026-01-23T17:33:33+05:30Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems store your most valuable business data. That’s exactly why hackers target them, making CRM security a critical priority for any organization. Understanding what hackers look for first in your CRM can help you protect customer information, avoid data breaches, and keep your business safe. Hackers don’t randomly attack systems—they follow patterns. They search for weak points that give quick access to customer data, financial records, and internal operations. In this blog, we’ll break down these risks in simple words and explain how improving your CRM security can help reduce them.
Top CRM Security Weaknesses Hackers Look for First
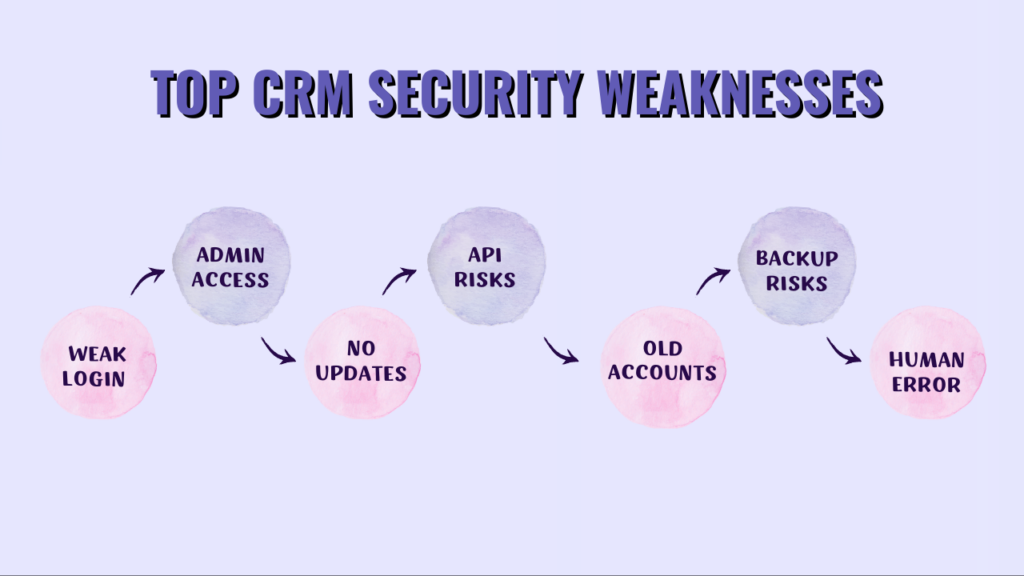
1. Weak Login Credentials (First Thing Hackers Check)
Weak login credentials are the first thing hackers test when trying to break into a CRM system. Simple passwords like common words, names, or number patterns are easy to crack using automated tools. Shared CRM logins make attacks even easier because one stolen password gives full access. Strong, unique passwords combined with two-factor authentication greatly reduce CRM hacking risks. This is one of the most common causes of CRM data breaches.
2. Admin-Level Access Without Restrictions
Admin accounts are highly valuable targets for hackers because they provide full system control. If one admin account is compromised, hackers can export customer data or delete CRM records. Many companies give too many users admin rights without reviewing them regularly. This increases the impact of a single security failure. Limiting access based on job roles is a core CRM security best practice.
3. Unpatched CRM Software
Outdated CRM software often contains known security vulnerabilities. Hackers actively search for systems that have not installed the latest updates. Missing patches allow attackers to exploit bugs that are already documented. Delaying updates increases the chances of a CRM data breach. Keeping your CRM software up to date helps close these security gaps quickly.
4. Poor API and Integration Security
Modern CRMs rely on APIs to connect with email, payment, and marketing tools. Hackers often attack these integrations instead of the main CRM system. Weak API keys or open permissions can expose sensitive customer data. Poorly secured integrations make unauthorized access easier. Securing APIs is critical for protecting connected CRM platforms.
5. Lack of Data Encryption
Without encryption, CRM data can be easily read if stolen or leaked. Hackers can exploit unprotected customer records and backups. Data encryption protects information while it is stored and while it is being transferred. Using HTTPS and SSL helps secure CRM communication. Encryption is essential for customer data protection and compliance.
6. Inactive or Forgotten User Accounts
Inactive CRM user accounts are often ignored but remain a major security risk. Former employees may still have access long after leaving the company. Test accounts and temporary logins are frequently forgotten. Hackers look for these weak entry points during attacks. Regular account reviews help prevent unauthorized CRM access.
7. Poor CRM Backup Security
CRM backups often store complete copies of customer and business data. If backups are not encrypted, hackers can easily exploit them. Online or publicly accessible backups are common attack targets. Many businesses forget to protect backup files properly. Securing CRM backups is critical for overall data security.
8. Phishing Attacks on CRM Users
Phishing attacks target employees rather than CRM software itself. Hackers send fake emails that trick users into sharing login details. Once credentials are stolen, attackers can access the CRM directly. Phishing is one of the most common CRM attack methods. Regular training helps employees recognize and avoid phishing threats.
9. No Activity Monitoring or Alerts
Without monitoring, suspicious CRM activity can remain hidden for long periods. Hackers rely on the lack of alerts to move quietly inside the system. Unusual logins, data exports, and permission changes often go unnoticed. Activity logs help detect early warning signs. Monitoring is essential for preventing serious CRM security incidents.
10. Lack of Security Awareness
Businesses with low security awareness are easier targets for hackers. The absence of policies and training increases the risk of human error. Employees may unknowingly expose CRM data through unsafe actions. Security is not just technical but also behavioral. A strong security culture helps prevent CRM breaches.
FAQs – What Hackers Look for First in Your CRM
1. What is the biggest CRM security risk?
The biggest CRM security risk is weak passwords and unrestricted admin access. Hackers often try simple or reused passwords first to gain entry. Admin accounts without proper limits give attackers full control once compromised. Using strong passwords and role-based access reduces this risk significantly.
2. Is cloud CRM more secure than on-premise CRM?
Cloud CRM systems can be very secure when properly configured. Reputable providers offer regular updates, encryption, and monitoring tools. However, security still depends on user settings and access control. A poorly configured cloud CRM can still be vulnerable to attacks.
3. Can small businesses be targeted by CRM hackers?
Yes, small businesses are frequently targeted by hackers. They often have fewer security controls and limited monitoring in place. Hackers see small companies as easier entry points with valuable customer data. CRM attacks do not only target large enterprises.
4. How often should CRM security be reviewed?
CRM security should be reviewed every 3 to 6 months. Reviews are also needed when employees join or leave the company. System updates and new integrations also require security checks. Regular reviews help identify risks before hackers exploit them.
5. How do I know if my CRM has been hacked?
Common signs include unusual login activity and unknown IP addresses. Missing or altered customer data is another warning sign. Unauthorized data exports or sudden system slowdowns may indicate a breach. Reviewing activity logs can help confirm a CRM security incident.

Conclusion
Knowing what hackers look for first in your CRM helps you prevent cyberattacks before they happen. CRM systems store sensitive customer and business data, making them a top target for hackers. By using strong passwords, limiting admin access, updating CRM software, and training employees, businesses can reduce security risks. Regular monitoring and security reviews further strengthen CRM protection. For businesses looking for a secure and reliable solution, Kenfra CRM provides robust security features and comes with a free trial. Protect your customer data, streamline your operations, and experience a safe CRM platform without any risk. In today’s digital world, CRM security is not optional — it’s essential.












Leave a Reply